Understanding The Dow Jones Average Index: A Comprehensive Guide
The Dow Jones Average Index is one of the most recognized and important indices in the world of finance. As a key indicator of market performance, it provides insights into the overall health of the U.S. economy and serves as a benchmark for investors. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of the Dow Jones Average Index, exploring its history, components, and how it impacts investors and the economy at large.
The Dow Jones Average Index, often referred to simply as the Dow, has been a critical part of financial markets since its inception. Established in 1896 by Charles Dow, it was originally designed to track the performance of 12 major companies in the U.S. Today, the index comprises 30 significant publicly traded companies, representing various industries and sectors. Understanding this index is essential for both novice and experienced investors as it can influence investment decisions and market strategies.
Throughout this article, we will discuss the various facets of the Dow Jones Average Index, including its calculation, significance, and how it compares to other indices like the S&P 500 and NASDAQ. Whether you are an investor looking to enhance your portfolio or simply curious about financial markets, this guide aims to provide valuable insights and information.
Table of Contents
- 1. History of the Dow Jones Average Index
- 2. Components of the Dow Jones Average Index
- 3. Calculation Method of the Dow Jones Average Index
- 4. Significance of the Dow Jones Average Index
- 5. Comparison with Other Indices
- 6. Investing Strategies Related to the Dow
- 7. Impact on the Economy
- 8. Future of the Dow Jones Average Index
1. History of the Dow Jones Average Index
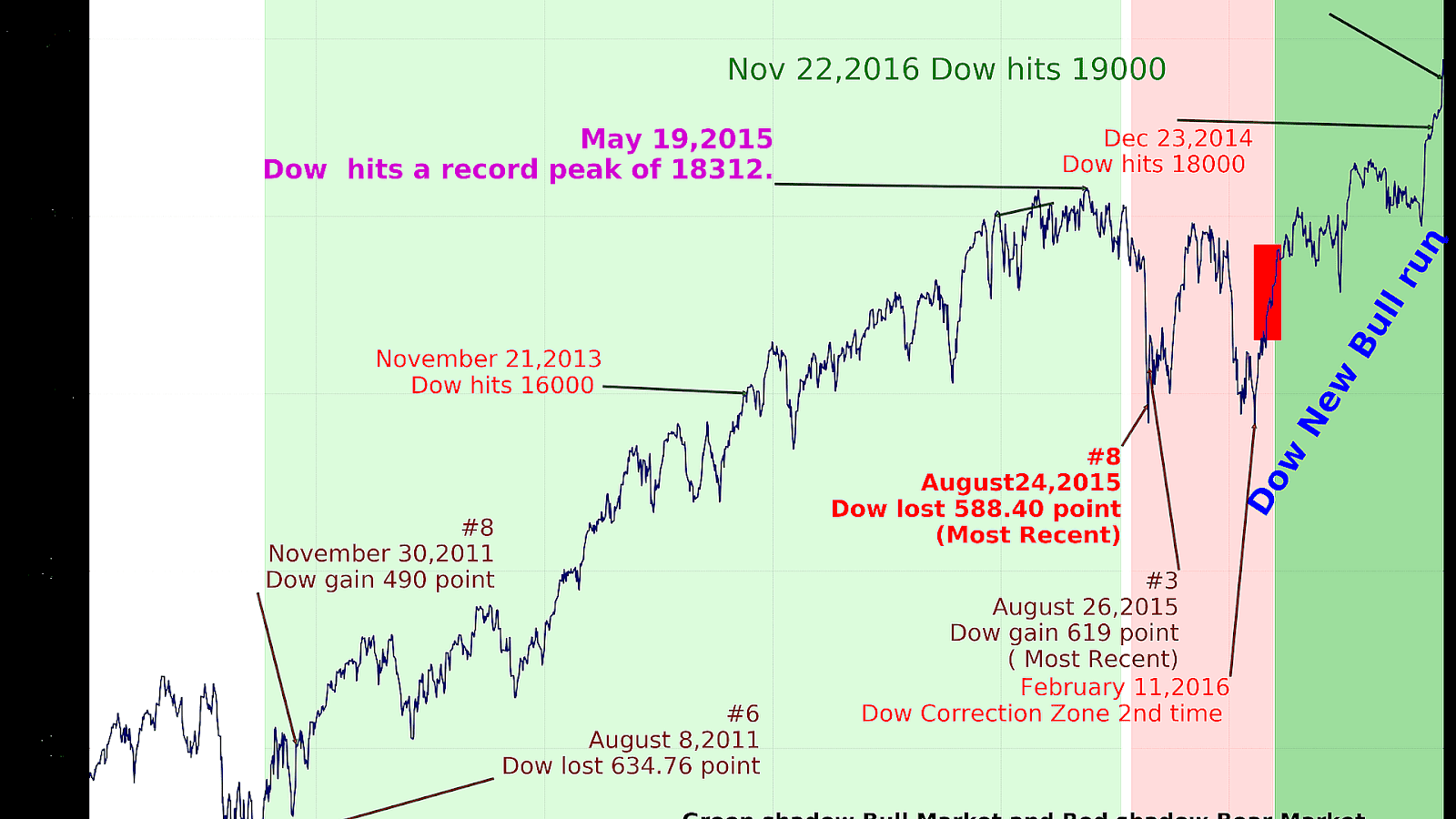
The Dow Jones Average Index was created in 1896 as a tool to measure the performance of the U.S. stock market. Charles Dow, who was a co-founder of Dow Jones & Company and the Wall Street Journal, initially calculated the index using the stock prices of 12 industrial companies. Over the years, the index has evolved significantly, expanding its components and adapting to changes in the economy.
In 1928, the index was expanded to include 30 companies, a practice that continues to this day. The index reflects the performance of blue-chip companies, which are known for their stability and reliability. Major events in history, such as the Great Depression, the dot-com bubble, and the 2008 financial crisis, have all influenced the trends and movements of the Dow.
Today, the Dow Jones Average Index is not only a critical tool for investors but also a barometer for the overall economic climate in the United States. It is widely reported in the media and serves as a key indicator for market sentiment.
2. Components of the Dow Jones Average Index
The Dow Jones Average Index consists of 30 prominent publicly traded companies, often referred to as "blue-chip" stocks. These companies are major players in their respective industries and are known for their financial stability and reliability. The components of the Dow can change over time; for instance, companies may be added or removed based on their economic performance and relevance.
Current Components of the Dow Jones Average Index:
- Apple Inc. (AAPL)
- Boeing Co. (BA)
- Coca-Cola Co. (KO)
- Disney (DIS)
- Goldman Sachs Group Inc. (GS)
- IBM (IBM)
- Microsoft Corp. (MSFT)
- UnitedHealth Group (UNH)
- Visa Inc. (V)
- Johnson & Johnson (JNJ)
- McDonald's Corp. (MCD)
- Procter & Gamble Co. (PG)
- 3M Co. (MMM)
- American Express Co. (AXP)
- Intel Corp. (INTC)
- Chevron Corp. (CVX)
- Walgreens Boots Alliance (WBA)
- Home Depot (HD)
- Exxon Mobil Corp. (XOM)
- Salesforce.com Inc. (CRM)
3. Calculation Method of the Dow Jones Average Index
The calculation of the Dow Jones Average Index is unique compared to other market indices. It uses a price-weighted methodology, which means that stocks with higher prices have a greater influence on the index's overall movement. The formula used to calculate the index is relatively straightforward:
Dow Jones Average = (Sum of stock prices of all 30 companies) / Divisor
The divisor is a figure that adjusts the index for stock splits, dividends, and other factors, ensuring that the index remains accurate and relevant over time. Because of this calculation method, a significant change in a high-priced stock can lead to a more substantial impact on the index compared to a change in a lower-priced stock.
4. Significance of the Dow Jones Average Index
The Dow Jones Average Index serves several critical functions in the financial markets:
- Market Indicator: It provides a snapshot of the overall health of the U.S. stock market and economy.
- Investor Benchmark: Investors often use the index as a benchmark to evaluate the performance of their portfolios.
- Media Reference: The index is frequently referenced in financial news, helping to inform the public about market trends.
Understanding the significance of the Dow is crucial for investors making informed decisions. Movements in the index can influence investor sentiment and market behavior, impacting buying and selling strategies.
5. Comparison with Other Indices
While the Dow Jones Average Index is one of the most well-known indices, it is essential to compare it with other significant indices, such as the S&P 500 and NASDAQ Composite Index.
Key Differences:
- Index Composition: The Dow consists of 30 companies, while the S&P 500 includes 500 of the largest U.S. companies. The NASDAQ Composite includes over 3,000 stocks, primarily technology-focused.
- Weighting Method: The Dow is price-weighted, while the S&P 500 and NASDAQ are market capitalization-weighted, meaning larger companies have a more significant impact on these indices.
- Sector Representation: The Dow's composition is more focused on traditional industries, while the NASDAQ tends to include more tech and growth-oriented companies.
Investors often analyze multiple indices to get a comprehensive view of market performance and trends.
6. Investing Strategies Related to the Dow
Investing strategies involving the Dow Jones Average Index can vary widely. Here are some common approaches:
- Buy-and-Hold Strategy: Many investors choose to invest in Dow components for the long term, benefiting from potential appreciation and dividends.
- Index Funds and ETFs: Investors can invest in index funds or exchange-traded funds (ETFs) that track the performance of the Dow, providing diversified exposure to its components.
- Technical Analysis: Some traders use technical analysis of the Dow's movements to make short-term investment decisions.
Understanding these strategies can help investors align their goals with the performance of the Dow.
7. Impact on the Economy
The Dow Jones Average Index has a significant impact on the broader economy. As a leading indicator, movements in the index can influence consumer confidence, corporate investment decisions, and economic policy. A rising Dow often correlates with increased consumer spending and business investment, while a declining index may signal economic concerns.
Additionally, the index's performance can affect retirement accounts, mutual funds, and other investment vehicles that rely on its movements. Therefore, understanding its implications is crucial for both individual and institutional investors.
8. Future of the Dow Jones Average Index
The future of the Dow Jones Average Index will likely be influenced by various factors, including economic trends, technological advancements, and shifts in investor sentiment. As the economy evolves, so too may the companies within the index. Investors must stay informed about these changes to make sound investment decisions.
Moreover, as new industries emerge, there's potential for increased volatility in the index's performance
Married To Real Estate: A Comprehensive Guide To Building Your Future
Mayweather Net Worth: An In-Depth Analysis Of His Wealth And Success
Buggy The Clown Live Action: A Deep Dive Into The Iconic Character